Digitising the invoice process has helped many organisations streamline their accounts processing workflows and deliver huge cost savings — in fact research has shown electronic invoicing can save between 60 and 80 per cent compared to paper invoicing processing. It’s also become an essential part of de-risking accounts payable, and today is foundational to building an intelligent finance function. Check out our guide to electronic invoicing to find out why.
Definition: What is electronic invoicing?
Electronic invoicing, or e-invoicing, describes issuing and receiving invoices in an electronic format, enabling businesses to streamline their billing processes. Unlike traditional paper invoices, electronic invoices are generated, transmitted, and stored digitally, often using specific formats and standards to ensure interoperability and compliance with various regulatory requirements.
The process of e-invoicing includes the entire lifecycle of an invoice, from creation and delivery to receipt and archiving, all in a digital format. They are created using software applications that generate the document in a standardised electronic format. Common formats include XML, PDF/A-3 (with embedded XML), and other industry-specific formats.
The electronic invoice is then transmitted from the sender to the recipient through secure electronic channels. This can involve direct transmission via email, electronic data interchange (EDI) systems, or specialised e-invoicing platforms and networks. The recipient’s system receives the electronic invoice and automatically integrates it into their accounts payable system. Once received, the electronic invoice is validated for accuracy and compliance with relevant standards and regulations. Automated validation checks can include verifying the supplier’s details, matching the invoice with purchase orders, and ensuring that the invoice meets tax compliance requirements.
As a last step, both the sender and the recipient archive the electronic invoice digitally, ensuring it is stored securely and can be easily retrieved for future reference, audits, or regulatory compliance.
European Commission standard on e-invoicing
You may have heard of EN16931 before. The European Commission has established this norm as a standard for e-invoicing in public procurement. It is designed to ensure interoperability and standardisation across different member states and their respective systems, facilitating cross-border trade within the European Union.
Key aspects of the EN16931:
Semantic data model: EN16931 specifies the mandatory and optional data elements that an invoice must contain, such as the supplier’s and buyer’s details, invoice line items, tax information, and total amounts.
Syntax mapping: The standard provides guidelines for mapping the semantic data model to various syntaxes, such as UBL (Universal Business Language) and CII (Cross-Industry Invoice). This ensures that electronic invoices can be generated and interpreted consistently, regardless of the underlying technology or platform.
Compliance and validation: EN16931 sets out rules for compliance and validation to ensure that electronic invoices meet legal and fiscal requirements across different jurisdictions within the EU. This includes provisions for digital signatures and other security measures to authenticate the invoice’s integrity and origin.
Interoperability framework: The standard promotes interoperability between different e-invoicing systems and platforms, enabling seamless exchange of electronic invoices between businesses and public administrations across the EU. This is crucial for reducing trade barriers and enhancing the efficiency of public procurement processes.
What is an e-invoice?
To clarify what an e-invoice truly is, it is helpful to understand what it is not. Of course, paper invoices, including those that were sent through fax machines and digitised afterwards, can not be called e-invoices. They originate as paper documents and lack the inherent digital structure required for automated handling. The reason: Scanned images of invoices, whether in JPG, TIFF, or other image formats, do not qualify as e-invoices. These images cannot be processed by automated systems without additional steps like OCR (Optical Character Recognition). And even OCR-scanned invoices do not qualify as true e-invoices.
Documents created in PDF or Word formats are also not considered true e-invoices unless they provide a structured data layer that can be directly processed by accounting systems. The same applies to HTML invoices displayed on a webpage or sent within an email body. They are usually unstructured and cannot be directly imported into financial systems for automated processing.
So what is a true e-invoice then?
An e-invoice is a digitally created and formatted document that contains structured data, allowing for automatic processing by both the sender’s and receiver’s financial systems. Standardised formats such as XML, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), or UBL (Universal Business Language) are typical for e-invoices. They ensure that the invoice data is machine-readable and can be integrated into various accounting software without the need for manual intervention.
Documents created in PDF or Word formats are also not considered true e-invoices unless they provide a structured data layer that can be directly processed by accounting systems. The same applies to HTML invoices displayed on a webpage or sent within an email body. They are usually unstructured and cannot be directly imported into financial systems for automated processing.
What Data Must Be Included in an e-invoice?
An e-invoice must include specific data elements to ensure it meets legal, fiscal, and business requirements.
Invoice number
Invoice date
Due date
Supplier name, address and tax identification number
Buyer name, address and tax identification number
Details of goods or services (description, quantity, unit price, subtotal and total amount, totals and tax)
Bank details, additional terms and conditions
Additional Information can include a purchase order number, delivery information, and further comments and notes. By including all these elements in a standardised format, your e-invoice will be accurate and compliant with various business and regulatory requirements.
Common e-invoicing standards and e-invoicing formats
Here’s an overview of some common e-invoicing standards and formats:
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation):
- Human-readable and easy to understand.
- Compact and lightweight, making it suitable for web-based transactions.
- Widely supported across various programming languages and platforms.
XML (eXtensible Markup Language)
Highly structured and flexible, allowing for detailed data representation.
Extensively used in business-to-business (B2B) transactions.
Supports schema validation to ensure data integrity and compliance with standards.
Peppol BIS (Pan-European Public Procurement Online Business Interoperability Specifications)
Ensures compliance with European e-invoicing regulations.
Promotes interoperability and standardisation across borders.
Secure and reliable transmission of invoices through the Peppol network.
EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport)
Well-established and globally recognised standard.
Supports a wide range of business processes and document types.
Enables automated processing and integration with legacy systems.
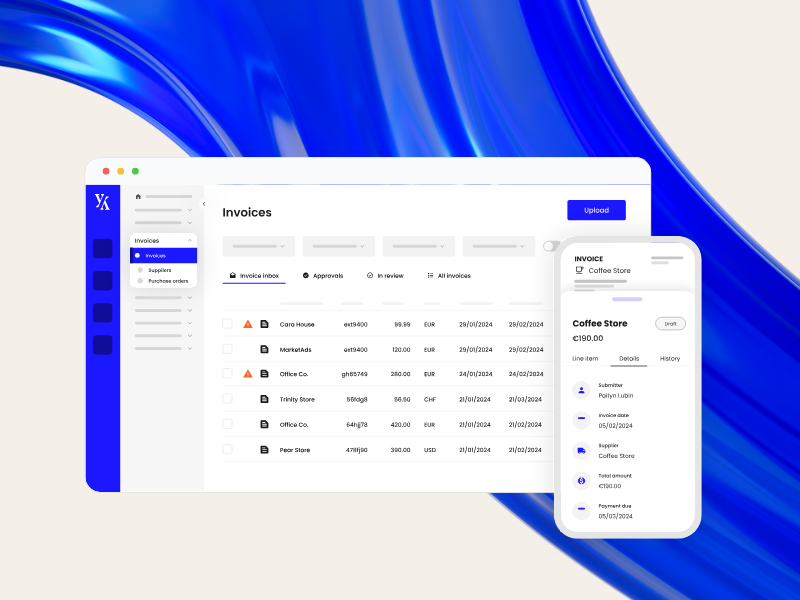
Yokoy Invoice
Process invoices automatically
Streamline your accounts payable process to manage invoices at scale and pay suppliers on time with Yokoy’s AI-powered invoice management solution.
Benefits of e-invoicing summarised
It is safe to say that e-invoicing offers several advantages over traditional paper-based invoicing. Let us explore the benefits in detail:
E-invoices save your company money and reduce human errors
In fact, e-invoicing can save costs by reducing the need for paper, postage, and printing and eliminating costs related to physical storage. On top of that, labour costs are reduced since automated processes minimise the need for manual data entry, handling, and correcting errors that occur with manual processing.
E-invoices are a great time-saver, improve cash flow, and allow for real-time data access
The time required to generate, transmit, and process e-invoices is considerably less than that for paper invoices. The result: Payments can be issued and received much faster, positively affecting your cash flow. Additionally, the ability to automate the matching of invoices with purchase orders and delivery receipts facilitates quicker dispute resolution. Digital storage of invoices also ensures that they can be accessed and retrieved instantly, speeding up audits and other processes requiring historical invoice data.
Give fraudsters a hard time
E-invoicing enhances the detection and prevention of fraudulent activities through built-in verification mechanisms such as digital signatures and encryption. These features help ensure that invoice data is authentic and has not been tampered with. Additionally, comprehensive audit trails in e-invoicing systems allow for detailed tracking of all actions related to invoices, making it easier to identify and investigate suspicious behaviour.
Structured data streamlines the invoicing process
E-invoices are generated in standardised formats such as XML or JSON, which ensures that the data is structured and machine-readable. This structuring facilitates seamless integration with existing accounting and ERP systems. Therefore, e-invoicing is an essential part of automating the entire invoicing lifecycle, from creation to archiving, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Secure data exchange for maximum compliance
E-invoicing platforms employ advanced encryption methods to secure data during transmission, protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access. Additionally, digital signatures and other authentication methods ensure that the origin and integrity of the invoice data are verified, enhancing the overall security of the invoicing process. Moreover, e-invoicing solutions often include features designed to ensure compliance with local and international regulations, including tax and reporting requirements.
Blog article
Automated Invoice Processing: Process Steps and How to Get Started
What is invoice processing automation all about? Learn how AI-powered invoice automation works and how it can help you save time, reduce risks, and improve your view of cash flow.

Mauro Spadaro,
Product Manager
From paper invoices to electronic invoicing
The traditional invoicing process with paper invoices involved several manual steps: First, the supplier would manually create the invoice, often using word processing or spreadsheet software, and print it out on paper. The printed invoice would then be sent to the buyer via postal mail or fax. This involved addressing envelopes, affixing postage, and relying on postal services for delivery. Upon receiving the invoice, the buyer’s AP department would manually sort and open the mail, date-stamp the invoice, and log it into the accounting system. This could involve physically storing the invoice in filing cabinets.
AP staff would manually enter the invoice details into the company’s accounting or ERP system. This step was prone to errors, as human operators could easily mistype or misinterpret the data. The invoice would then go through an internal approval process. This might involve physically passing the invoice to various departments or managers for their signatures, which could lead to delays if any approvers were unavailable.
Once approved, the invoice would be scheduled for payment. This could involve writing checks or setting up bank transfers, and the supplier would be notified by mail once the payment was processed. After payment, the paper invoice and any associated documents would be filed away in physical storage for future reference or audit purposes. This required substantial space and organisation to maintain an accessible archive.
Why was this not helpful for an efficient AP process?
This entire process, from creation to archiving, involved numerous steps and took considerable time. Delays in postal delivery, manual data entry, and approval workflows often resulted in slow processing times, leading to late payments and missed early payment discounts. Mistakes in entering invoice details, misplacing documents, or incorrectly filing invoices could lead to payment discrepancies and additional administrative burdens to rectify the errors.
Of course, the costs associated with paper, printing, postage, storage, and labour were significant. Maintaining physical storage for invoices also required substantial space and resources, adding to overhead costs and a great environmental impact.
Moreover, tracking the invoice status was difficult, as it required manually checking with various departments or physically searching through files. Therefore, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and preparing for audits was challenging.
By adopting e-invoicing, businesses can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their AP processes, leading to better financial management and overall operational performance.
Make e-invoicing work: 5 steps to modern invoicing methods
Could the benefits of e-invoicing convince you to make the switch? Here’s a list of what to look out for when implementing e-invoicing.
Step 1: Integration into existing systems
When evaluating e-invoicing solutions, look for those that offer compatibility with your current software platforms. This will allow for automatic data synchronisation, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimising errors. Ensure that the e-invoicing solution can handle data import/export functions, integrate with your workflow, and support any required API connections.
Step 2: Check scalability
Evaluate whether the solution can handle an increasing invoice volume as your business grows. It should also support additional features and functionalities that may become necessary in the future, such as multi-currency support, multi-language capabilities, and the ability to manage complex invoice structures.
Step 3: Identify costs and potential savings
Consider the costs associated with implementing and maintaining an e-invoicing solution. This includes the initial setup fees, subscription or licensing costs, and additional upgrades or support charges. While evaluating these costs, consider the potential for cost savings the solution offers. We recommend conducting a cost-benefit analysis to determine the return on investment (ROI).
Step 4: Check compliance features
Different countries have varying requirements for electronic invoices, including specific formats, data elements, and archiving rules, so it is helpful to make sure that the e-invoicing solution you choose complies with all relevant regulations and standards, such as VAT requirements, e-signature mandates, and data protection laws.
Step 5: Does the solution offer a holistic approach?
The right solution should automate invoicing and enhance the entire AP workflow. Look for end-to-end automation features, from invoice creation and approval to payment and archiving. The solution should provide real-time visibility into invoice status, streamline approval workflows, and integrate with payment systems for faster processing. Additionally, it should offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities to provide insights into AP performance and help identify areas for further improvement.
Invoice processing with AI: The modern e-invoicing solution
Yokoy offers a comprehensive AI-powered e-invoicing solution that transforms the entire accounts payable process, enhancing efficiency and accuracy through automation.
Yokoy’s key features:
AI-based automation
End-to-end automation
Custom approval flows
Compliance and audit trails
Real-time reporting
Secure data exchange
Multi-entity support
Mobile Accessibility
The system automatically captures, validates, and authorises invoices, significantly reducing the time and effort required for invoice processing. This end-to-end automation covers everything from invoice receipt to sending them for payment, ensuring that all steps are handled efficiently within a single platform.
Invoicing automation with Yokoy’s AI
Here’s a detailed look at how Yokoy’s spend management AI works to streamline invoice processing.
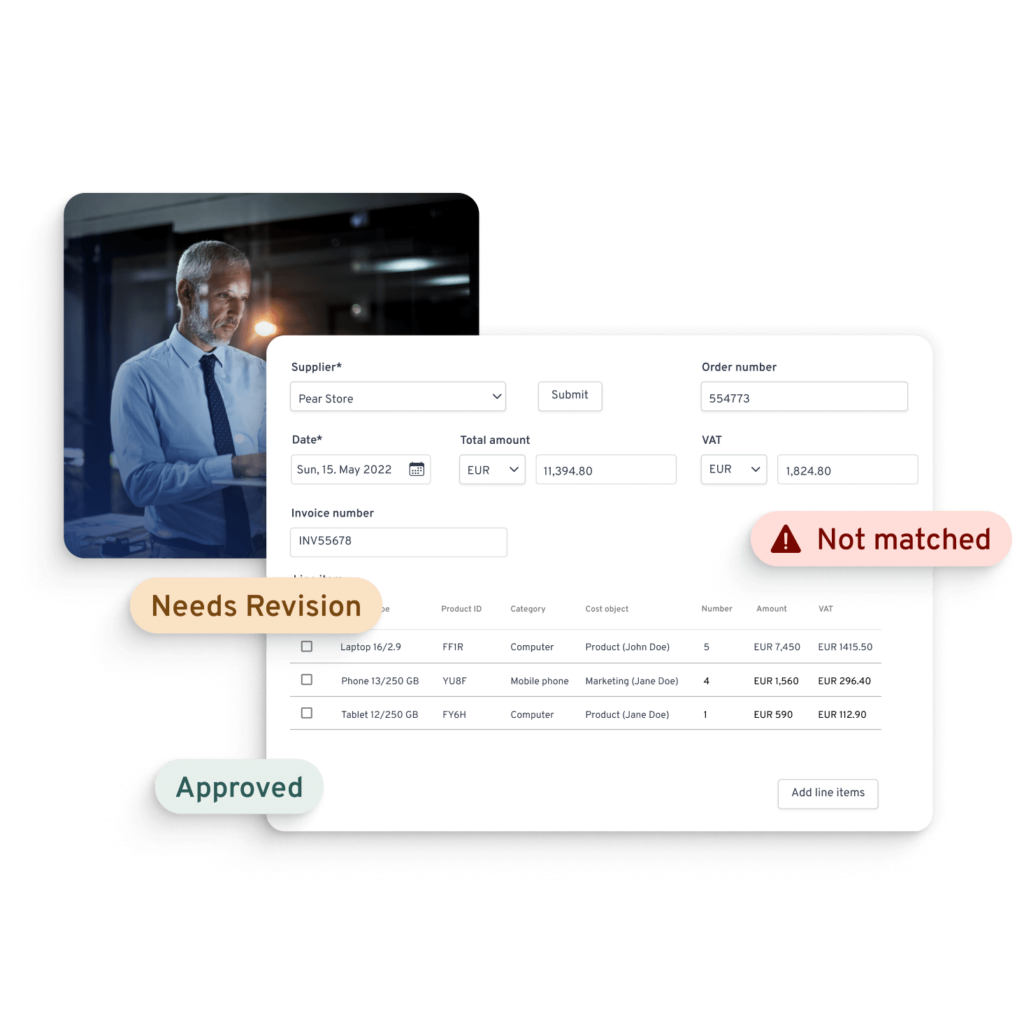
AI-based data extraction and validation:
When an invoice is received, AI instantly understands the structure of. the invoice and adds context, for example identifying the company address, VAT number, or individual line items based on its in-depth underdstanding of invoice data.
AI parses the extracted data, cross-checks it against purchase orders, contracts, company policies, or regulatory requirments
By automating data entry and validation, Yokoy minimises human errors and ensures data integrity.
Smart coding uses AI to automatically code line items on each invoice by recognising the type of expense, and then coding it based on what it’s learned from how people have handled similar items in the past.
Automated workflow management:
Users can define multi-level approval hierarchies and set criteria for different types of invoices.
The system sends real-time notifications to approvers, reducing delays and ensuring timely processing.
The AI can identify discrepancies and exceptions, routing these cases to the relevant individuals for manual review.
Enhanced compliance and audit trails:
Automated compliance checks ensure that invoices meet local and international regulatory standards.
Every action on an invoice is logged, providing a transparent and accessible audit trail for regulatory and internal reviews.
Real-time reporting and analytics:
The platform’s reporting tools offer comprehensive visibility into invoice statuses, payment cycles, and overall AP performance.
Users can access real-time dashboards showing the status of invoices and overall AP metrics.
Detailed reports on processing times, approval rates, and payment cycles help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Easy integration with existing systems:
All invoice data is stored centrally, facilitating easy access and management.
Integration ensures that all departments have access to up-to-date financial information, fostering better collaboration.
Invoice data is automatically synchronised with ERP and accounting systems, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and enabling better cashflow management by booking spend in the system when an invoice comes in, rather than waiting for a payment to go out.
Next steps
Do you want to learn more about Yokoy’s invoice management features and how you can automate your e-invoices? Simply get in touch and test our powerful tools for yourself.
Simplify your invoice management
Related content
If you enjoyed this article, you might find the resources below useful.


