Home / Invoice Coding in Accounts Payable: Process and Challenges
Invoice Coding in Accounts Payable: Process and Challenges
- Last updated:
- Blog
Product Marketing Manager, Yokoy
While it may seem like a routine task, the impact of invoice coding on financial operations is more significant than you might think.
In a manual process, where data in entered manually, the risk of errors is extremely high.
- According to the Institute of Finance and Management (IOFM), manual invoice processing can have an error rate as high as 8% to 12%.
- A study by PayStream Advisors found that manual invoice processing can result in an error rate of around 3% to 5%.
The cost of correcting errors in manually processed invoices can be substantial. According to the same sources, resolving an invoice error can cost around $53.
Surprised? You’re not alone.
In this article, we explore the traditional invoice coding process in accounts payable, including the challenges of manually coding invoices and the benefits of automating invoice processing.
What is invoice coding in accounts payable (AP)?
Invoice coding in accounts payable (AP) is a systematic method of assigning unique codes or identifiers to invoices. Just as different items have specific categories on store shelves, each expense in your financial records has its designated code, forming a comprehensive coding system.
Invoice codes help categorize expenses, allocate costs to specific cost centres or projects, and facilitate seamless tracking and reporting.
For instance, office supplies might have code “OS,” while travel expenses are “TR.”
In larger organisations or projects with multiple teams, invoice coding helps attribute costs to specific departments or projects. For example, if your IT department is working on a software upgrade, their expenses can be assigned a unique IT code.
Essentially, it’s the financial equivalent of organising your closet – ensuring everything has its designated place.
Why do you code invoices?
Now, you might be wondering, why go through the trouble of assigning codes to invoices?
The answer lies in the complexity of modern business operations. With a staggering 77% of companies experiencing fraud through manual processes, ensuring accuracy and accountability is paramount.
Invoice coding acts as a crucial control mechanism. It not only streamlines the payment approval process but also helps detect errors and inconsistencies early on.
In fact, according to a recent survey by the Institute of Finance and Management (IOFM), efficient invoice coding can reduce error rates by up to 40%.
So, what’s the big picture? What is invoice coding used for?
Invoice coding isn’t just about neat categorisation; it’s about harnessing the power of data.
When done right, it empowers finance professionals with actionable insights, enabling informed decision-making. In a world where data drives success, efficient invoice coding is the key to unlocking your organisation’s financial potential.
Now that we’ve set the stage, let’s explore the topic further, starting with traditional methods and gradually venturing into the realm of automation and innovation.
Check out our newsletter
Don't miss out
Join 12’000+ finance professionals and get the latest insights on spend management and the transformation of finance directly in your inbox.
Traditional invoice coding methods
Traditional invoice coding methods have been the bedrock of accounts payable for decades. They involve a step-by-step, manual process to assign codes to invoices. Let’s walk through this age-old procedure:
Receipt and review: The journey begins when a new invoice arrives. The accounts payable team responsible for coding the supplier invoice reviews the data meticulously. They examine every line item to understand the nature of the expenses.
Category identification: Next, they determine the appropriate expense categories or cost centers. This involves identifying if it’s an office supply purchase, travel expenses, equipment maintenance, or any other relevant category.
Code assignment: Once the category is established, the finance professional assigns a specific code to the invoice. These codes are often alphanumeric and are unique to each expense category. For example, “OS-001” for office supplies or “TR-002” for travel expenses.
GL code integration: After assigning the primary code, the finance professional maps it to the General Ledger coding. The GL code is a critical component of financial tracking, as it links the expense to the corresponding general ledger account.
Documentation: The vendor invoice, along with its code and GL code assignment, is recorded for future reference and audit purposes.
Approval and payment: Once coded, the invoice goes through the regular validation and approval process, and if all is in order, it proceeds for payment. Depending on the structure of the AP team, the approval workflow can involve multiple stakeholders.
This manual coding process, while suitable for smaller organisations, is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially when the AP team processes large volumes of invoices every day.
Human errors in coding can lead to misallocation of expenses, which can have a cascading effect on financial reporting and budget management. Of course, removing manual work from this process can significantly improve efficiency and reduce error rates.
We’ll look at how automation can help in the next sections, but you can learn about different invoice capture methods here.
How do you write an invoice code?
Writing an invoice code requires precision and consistency to effectively categorise and track expenses. However, the process can vary depending on whether you’re coding an invoice with or without a purchase order (PO).
Please note: This overview describes the manual process. However, the invoice processing workflow can be fully automated, starting from the invoice capture step and all the way to validating, approving, and paying the invoice.
We’ve detailed the topic in the article below.
Blog article
Automated Invoice Processing: Process Steps and How to Get Started
What is invoice processing automation all about? Learn how AI-powered invoice automation works and how it can help you save time, reduce risks, and improve your view of cash flow.

Mauro Spadaro,
Product Manager
Coding a non-PO invoice
The traditional coding process for non-PO invoices goes as follows:
Review the invoice: Start by thoroughly reviewing the invoice data. Identify the nature of the expenses and determine the appropriate expense category. This step is crucial in the absence of a predefined structure like a PO.
Select a coding format: Choose a coding format that aligns with your organization’s conventions. It could be a combination of letters and numbers, such as “TR-001” for travel expenses or “OS-002” for office supplies.
Assign a unique code: Based on the expense category, assign a unique code to the invoice. Make sure each code is distinct and doesn’t overlap with other codes in the same category.
Link to GL Code: Connect the assigned code to the corresponding General Ledger (GL) code. This linkage ensures that the expense is recorded accurately in your financial records.

Coding an invoice with a Purchase Order
When you have a purchase order, the coding process becomes more streamlined:
Refer to the PO: Start by referencing the purchase order associated with the invoice. The PO provides a structured format and predefined categories for coding.
Verify accuracy: Ensure that the invoice matches the details specified in the PO. Check for discrepancies and reconcile any differences between the PO and the invoice.
Use PO codes: In most cases, the PO will already contain specific codes or identifiers for expense categories. Utilize these codes for consistency and alignment with the original purchase order.
Link to GL code: Connect the PO-based code to the corresponding General Ledger (GL) code, just as you would with invoices without a PO. This step ensures that the expense is accurately recorded in your financial records.
Document the process: Maintain thorough documentation, including a copy of the invoice, the PO, the assigned code, the GL code linkage, and any relevant notes or comments.
Ensure compliance: Verify that your coding process complies with your organization’s internal policies and accounting standards, especially when working with purchase orders.
By following these steps, you can effectively write an invoice code whether you have a purchase order as a reference or need to code an invoice without one.
Scaling problems: The trouble with GL coding
As businesses expand and operations grow, they often encounter a formidable challenge in the form of scaling. One such challenge that becomes increasingly evident as organisations scale is the intricacy of General Ledger (GL) coding.
Here, we dissect the issues that arise when relying on traditional GL coding methods:
- Complexity amplified: With growth comes complexity. More transactions, more expense categories, and more departments mean an ever-expanding web of GL codes. Maintaining this complexity manually can lead to errors and confusion.
- Increased error rates: As the volume of transactions grows, so does the potential for human error. Even minor mistakes in GL coding can have far-reaching consequences, impacting financial reporting and decision-making.
- Time-consuming: Traditional GL coding is a labor-intensive process. As your organisation scales, dedicating significant manpower to this task becomes impractical. This time could be better utilised in value-added financial analysis.
- Lack of real-time visibility: Scaling organisations need real-time financial visibility. Traditional GL coding often lags behind, causing delays in accessing critical financial data.
- Limited adaptability: When faced with rapid growth or changes in business strategy, existing GL codes may become inadequate. Adapting and expanding codes to meet new requirements can be a cumbersome and inefficient process.
How does automated invoice processing work?
AP automation changes the way businesses handle invoices, increasing the efficiency and accuracy of invoice processing workflows.
Here’s how this game-changing technology operates:
Invoice capture
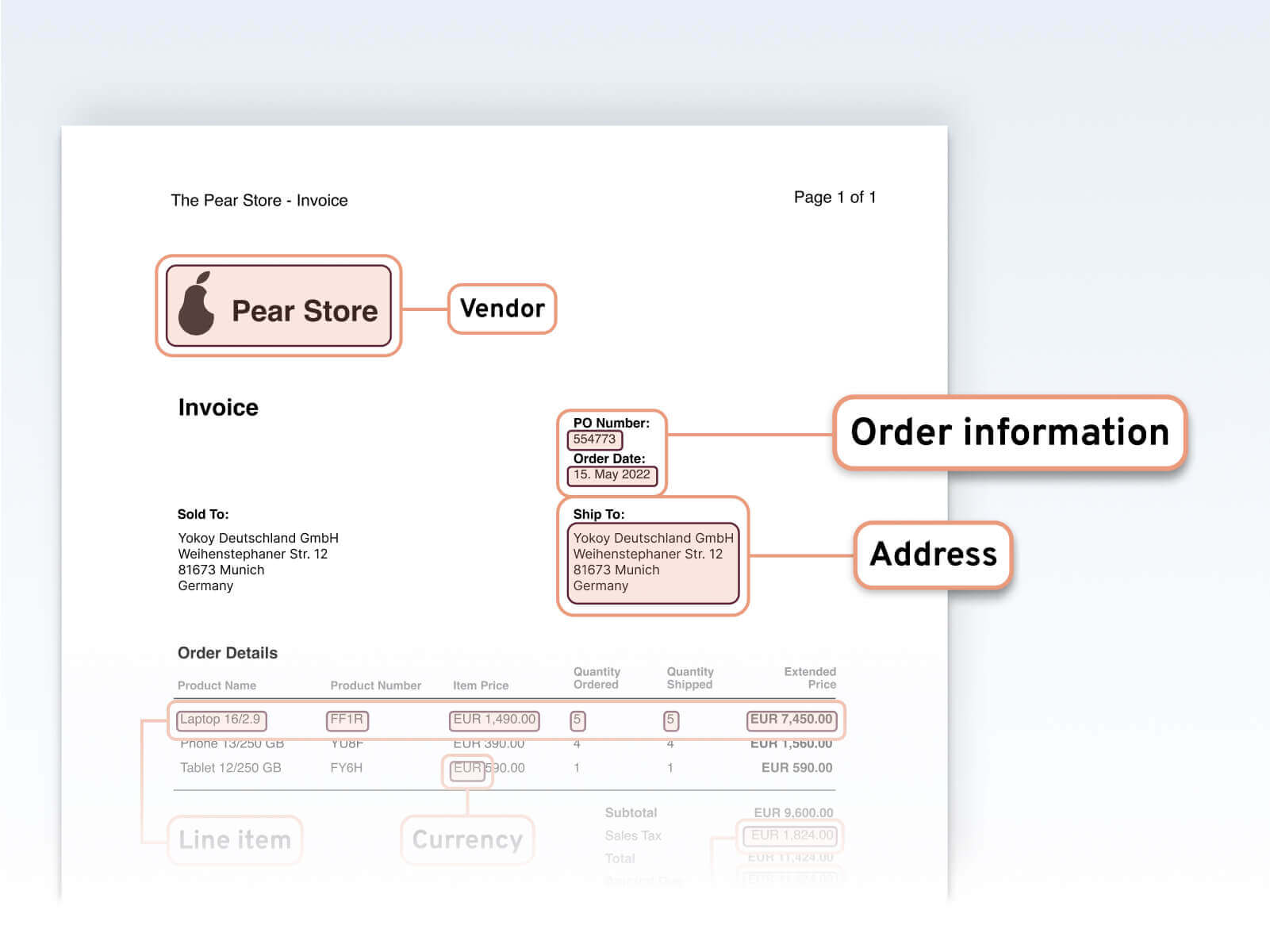
The process begins with the capture of incoming invoices. Automated invoice processing tools often use Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology to extract essential information from paper-based or electronic invoices. This data includes vendor details, invoice numbers, dates, line items, amounts, and relevant account codes.
Blog article
Invoice Capture Solutions: From Manual Processing to OCR and AI Technology
Unlock the power of invoice capture methods in finance, transitioning from manual processing to advanced Invoice OCR and AI technology.

Andreea Macoveiciuc,
Growth Marketing Manager
Data extraction
Once captured, the extracted data undergoes rigorous validation against predefined criteria, ensuring accuracy and compliance with your accounting system. Any discrepancies or anomalies are promptly flagged for review to maintain data integrity.
Invoice matching
Invoices are meticulously matched with associated purchase orders (POs) and receiving documents, aligning with predetermined purchase order codes and account codes.
Automated systems cross-reference invoice details with corresponding POs, verifying the accuracy of billed items, quantities, and relevant account numbers.
Blog article
How to Use Invoice Matching Technology to Improve Your Process Efficiency
See how invoice matching technology automates the 2- and 3-way matching of supplier invoices with POs and goods receipts, for an efficient AP process.

Mauro Spadaro,
Product Manager
Coding and GL mapping
The system intelligently assigns appropriate GL account codes to expenses and flawlessly maps them to General Ledger codes based on predefined rules within your accounting system. This meticulous coding ensures precise categorization for accurate financial reporting.
Invoice workflow automation
Automated workflows come into play, orchestrating the seamless routing of invoices through the approval process. Approvers, equipped with clear account codes and purchase order details, receive notifications to digitally review and approve invoices.
Exception handling: Should exceptions arise, predefined escalation procedures, inclusive of due dates, come into effect. For invoices with discrepancies or issues that can’t be automatically resolved, the system routes them to a designated team or individual for manual intervention.
Blog article
How to Automate Your Invoice Approval Workflows with Yokoy
A well-structured invoice approval workflow ensures accuracy, compliance, and transparency in the payment process. Here’s how Yokoy can help.

Mauro Spadaro,
Product Manager
Integration with ERP systems
Automated invoice processing solutions are seamlessly integrated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, fostering real-time data synchronicity. This deep integration eradicates the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and ensuring uniformity of account codes and account numbers across your organisation.
Audit trails and compliance
Automated systems maintain comprehensive audit trails, documenting every step of the invoice processing journey. This transparency aids in compliance and simplifies auditing processes.
Blog article
How to Ensure Regulatory Compliance With Automated Audit Trails
Learn how to get started with automated audit trails for monitoring financial transactions, detecting anomalies and ensuring compliance to internal controls and external regulations.

Lars Mangelsdorf,
Co-founder and CCO
Payment approval
Once an invoice receives final approval, it’s prepared for payment. Automated systems generate payment requests and initiate electronic payments, improving cash flow management.
Automated systems learn from historical data and improve over time. They become more accurate in data extraction, coding, and approval routing, streamlining the entire process further.
Next steps
As you consider the path forward for your accounts payable process, remember that automation is not just a tool; it’s a catalyst for efficiency, accuracy, and financial success. It’s the key to unlocking the full potential of your organisation’s financial operations, ensuring that due dates are met, account codes are precise, and your financial journey is smoother than ever before.
Yokoy’s AI-powered spend management suite helps global organisations streamline their accounts payable process, automating the entire invoice processing flow through functionalities like AI data capture, automated matching, and automated coding.
If you’d like to see what Yokoy’s invoice management module can do for your AP process, you can book a demo below.
See Yokoy in action
Bring your expenses, supplier invoices, and corporate card payments into one fully integrated platform, powered by AI technology.

Simplify your invoice management
Book a demoRelated content
If you enjoyed this article, you might find the resources below useful.


