Home / Mileage Allowance Payments: Complete Guide
Mileage Allowance Payments: Complete Guide
- Last updated:
- Blog
In many countries, travel by personal or corporate vehicles is a valid business spend. Tracking and managing reimbursable costs associated to vehicle travel against company policies or country rates is complex.
This guide will explain how to calculate and track mileage allowances so that your employees are effectively and correctly reimbursed according to the correct rates and policies
What is mileage allowance and why is it important?
Mileage allowance is essentially a sum of money that employees can receive from their employer which is based on the number of miles they drive for work-related purposes using their personal vehicle.
This allowance is important because it helps cover the cost of fuel, as well as contributing to general running costs such as maintenance for the vehicle.
What qualifies as business mileage?
Business mileage refers to the distance travelled for work-related purposes using a personal vehicle. It’s an essential aspect of financial tracking for businesses, ensuring that travel expenses related to vehicle use are accurately recorded.
Business mileage includes travel to various locations, such as client meetings, site visits, conferences, and other job-related tasks.
These business expenses are distinct from personal mileage, which pertains to trips made using a personal vehicle for personal reasons, like grocery shopping or commuting to and from a primary workplace.
To qualify as business mileage, a trip must meet certain criteria:
- Work-related destination: The trip’s primary purpose must be business-related. This could involve visiting clients, attending work meetings, or making deliveries.
- No personal detours: While en route to a business-related destination, any stops or detours for personal activities are not considered business mileage. For instance, if you drive to a client meeting but stop at a coffee shop for personal reasons, that portion of the trip isn’t business mileage.
Example business mileage conditions
- Home office to work site: If you work from a home office and need to travel to another location for work purposes, the mileage from your home to the work site is typically considered business mileage.
- Temporary work sites: If your job requires you to travel between temporary work sites, the mileage between these locations qualifies as business mileage.
Check out our newsletter
Don't miss out
Join 12’000+ finance professionals and get the latest insights on spend management and the transformation of finance directly in your inbox.
How is mileage allowance calculated?
- Standard mileage rate: Many countries offer a standard mileage rate set by the relevant tax authorities. This rate is designed to simplify the reimbursement process. However, in some countries the standard rate can vary dependent on the vehicle, fuel type or engine size. Employees need to accurately track their business mileage, and the employer reimburses them at the specified rate per mile. The standard rate considers various running costs, which usually includes fuel, plus a contribution towards general running costs.
- Actual expenses: Alternatively, some employers opt for a more detailed approach, where employees track and report their actual expenses associated with business mileage. This includes costs such as fuel, maintenance, registration, and depreciation. Employers then reimburse the employee based on these documented expenses.
Mileage allowances can differ depending on the industry, vehicle type, engine size, single or multiple vehicle occupancy, company policy, and location, among other things. In addition, sometimes rates can be stepped. As an example, the first 5,000 km driven could be claimed at one rate but all miles travelled over 5,000km but less than 20,000km could be claimed at a different rate.
Organizations often provide a standard rate for their employees, but there are also various government websites that list the relevant country rates.
Mileage tracking methods
Accurate mileage tracking is essential for businesses to reimburse employees and claim tax deductions. There are various methods to track business mileage:
- Manual logs: Maintenance of a physical logbook where the details are recorded, including the starting and ending odometer readings, destination, and purpose.
- Odometer readings: Recording of the starting and ending odometer readings for each trip. Plus, the maintenance of accurate records of the journey’s purpose and destination.
- Mobile apps: Many mobile apps allow mileage to be tracked automatically using GPS. These apps can record trip details and provide comprehensive reports.
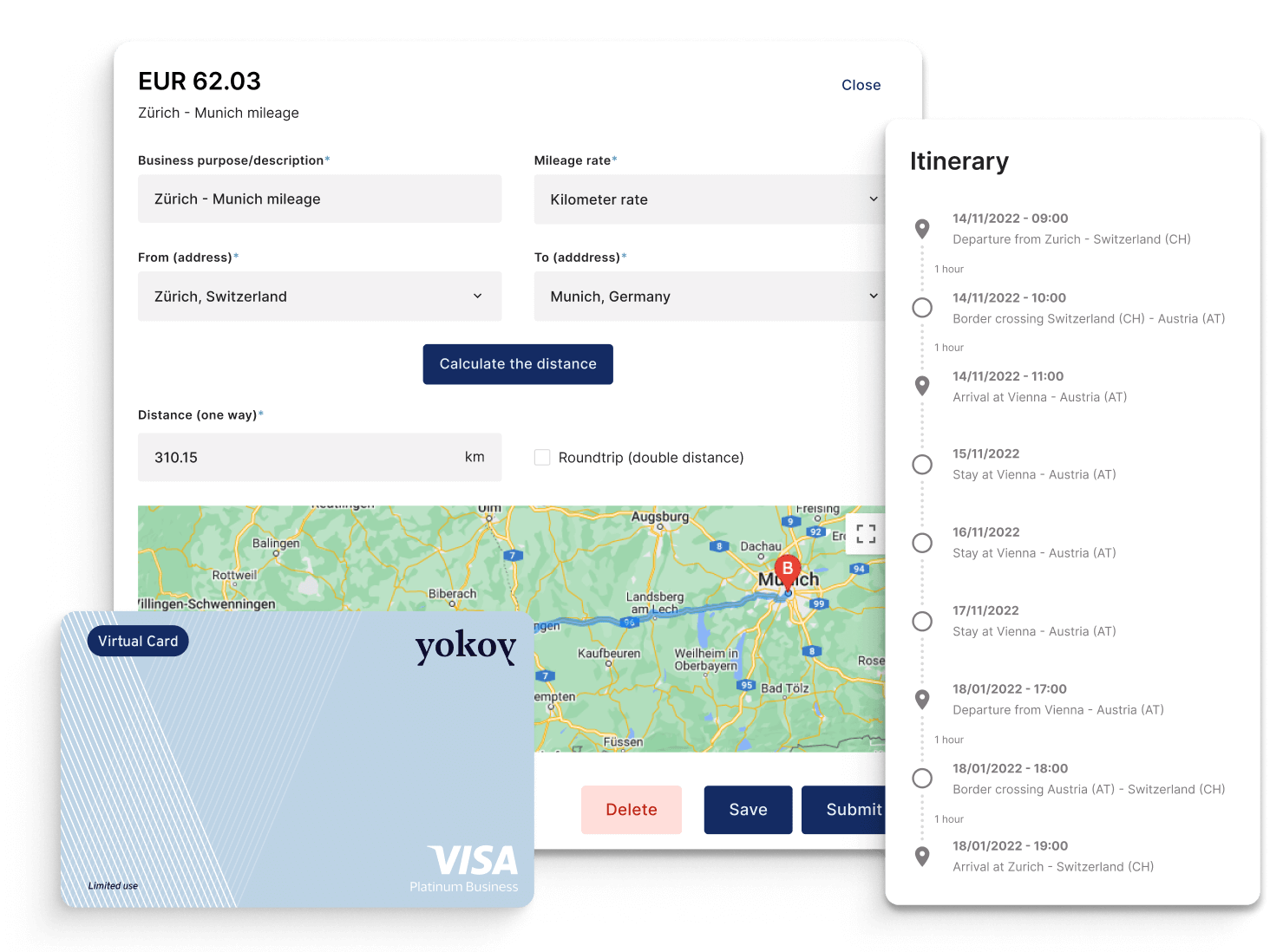
As an example, Yokoy’s travel, and expense module makes it very easy to track mileage. Multiple mileage rates can be set up as required to handle different scenario such as different reimbursement rates for electric versus combustion vehicles or for sole drivers versus drivers with additional passengers.
To calculate mileage reimbursements, Yokoy either uses Google Maps Directions API to automatically calculate the distance travelled between locations according to the best or fastest route. Or it can take the destination and arrival location, or address entered by the traveller, assign the correct mileage rate, and calculate the amount to be expensed. This is achieved by multiplying the submitted distance by the appropriate rate per kilometre (mile).
The employee simply needs to add the starting and destination address, and the rest is calculated automatically.
Who pays mileage reimbursements?
What are official mileage allowance rates?
Mileage allowance in Austria
The Austrian government recognises mileage allowances as a flat rate for all costs incurred for the usage of private vehicles for a business trip. This amount can be recognised for a maximum of 30,000 kilometres per calendar year.
Current mileage rates in Austria can be found here.
If an organisation decides to pay more than the government rates, the difference in amount is considered as taxable income and needs to be accounted for as such.
Compliance in Austria
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Austria, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.

Mileage allowance in Germany
Mileage expenses are aimed to cover the employee’s commute cost for business trips when using a private vehicle apart from the daily allowance/Per Diem. The German government recognises mileage allowances as a flat rate for all costs incurred for the usage of private vehicles for eligible business trips.
Current mileage rates in Germany can be found here.
If the employee receives an amount which is more than the recommended government rate, the additional amount will incur income tax.
For example, if the government recommends 0.30€ per kilometre, but the employee is reimbursed at 0.50€ per kilometre, the difference of 0.20€ per kilometre would be subjected to the relevant income tax and would need to be accounted for.
Compliance in Germany
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates – including the midnight rule and 3-month rule, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Germany, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.
Mileage allowance in Spain
Companies can reimburse employees to compensate for expenses incurred for the usage of private vehicle for business trips. In such cases, the employees are entitled to receive a “Mileage Allowance” which is recommended by the government.
Current mileage rates for Spain can be found here.
Mileage allowance in Switzerland
According to the Swiss code of obligations, employees are entitled to receive mileage allowances when they use their private vehicles for business purpose. Although there is not a flat rate that applies to all companies the Touring Club Swiss (TCS) publishes annual rates based on the type of vehicle. These rates are commonly used by businesses and can be found here.
Compliance in Switzerland
Stay up-to-date with rules and regulations around per diem rates, mileage allowances, proof of receipt, and VAT rates in Switzerland, while Yokoy keeps you audit-ready.

Mileage allowance in the UK
In the UK, mileage claims, and reimbursement are calculated and paid according to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) rules. In addition, if payments are over a certain amount the employer must report them to HMRC and deduct and pay the appropriate levels of tax. Understanding the relevant rules is essential to ensure that the employee receives accurate mileage reimbursement for business-related mileage, and that the correct tax is reported.
If a personal vehicle is used for business-related driving, the employer can reimburse the employee for business miles. This type of reimbursement, known as Mileage Allowance Payment (MAP), covers expenses like fuel, servicing, maintenance, and road tax for business-related driving.
In simple terms, if your trip is for business purposes, it qualifies for mileage reimbursement according to HMRC. Business trips include:
- Travel between the employees’ permanent workplace and temporary work locations (for example, visiting clients or suppliers).
- Travel between temporary workplaces.
- Travel between two workplaces within the same employment.
- Travel from the employees’ home to another workplace if their home is their permanent workplace due to job requirements.
Commuting from home to work or personal trips unrelated to business do not qualify for reimbursement.
Approved mileage rates issued by HMRC are here.
Is mileage allowance tax deductible?
Best practices for mileage allowance calculation
To ensure fair and accurate mileage allowance calculation, businesses should consider these best practices.
- Use reliable mileage tracking tools: Employers and employees should use reliable mileage tracking tools or apps to record and report business mileage to reduce errors and ensure accuracy.
- Compliance with tax regulations: Stay compliant with tax regulations and adhere to the standard mileage rates established by the relevant tax authorities.
- Regular reimbursement: Aim to reimburse employees promptly for their business mileage expenses.
Yokoy’s travel and expense management can help simplify mileage tracking for business expense management by automating the entire process, from mileage calculation, submission and claim to employee reimbursement.
In addition, once correctly configured the Yokoy expense solution can ensure that the correct mileage allowances are attributed to the employee supporting company compliance.
If you’d like to see how Yokoy can support your travel and expense management, book a demo below.
The information provided on this website is for information purposes only. All information on the website is provided in good faith, however we make no warranties of any kind regarding the accuracy, adequacy, validity or completeness of any information provided on the website or suitability for your specific business case. To discuss your specific business case please book a demo and we will arrange a call.
Yokoy Expense
Streamline your travel and expense management
Say goodbye to manual data entry, lost receipts, and complicated reimbursements. Yokoy handles everything from start to finish, for simple T&E management at any scale.
Simplify your invoice management
Book a demoRelated content
If you enjoyed this article, you might find the resources below useful.
Headline
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Headline
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Headline
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.


